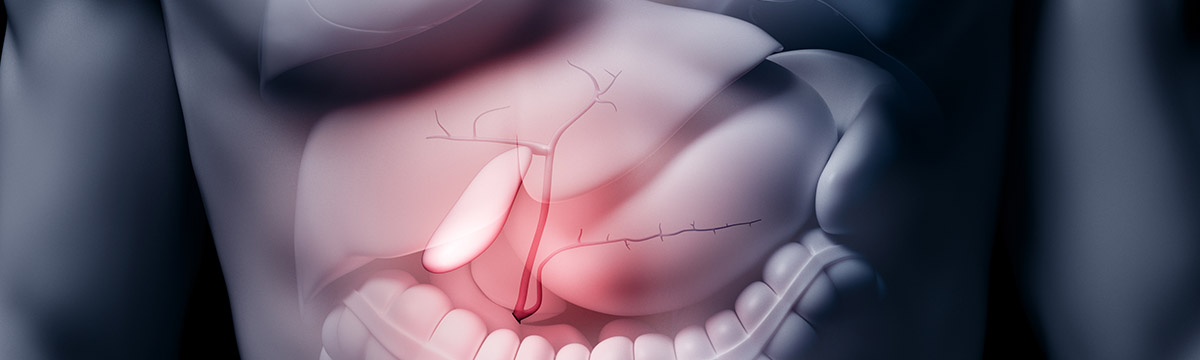
Gallbladder is located just below the liver. Its main function is to store bile which helps the body break down and digest fats. Bile liquid will be concentrated after gallbladder diseases and the deposition contains cholesterol and bile salts causing stones (Cholelithiasis) or infection of the gallbladder (Cholecystitis). Sudden pain is because of blocking the bile. To treat certain gallbladder problems, sometimes the organ must be surgically removed. These problems include:
- Biliary colicIt happens when something blocks the normal flow of bile from the gallbladder. One of the symptoms is pain, particularly after eating fatty foods. In this situation, surgery may be necessary..
- Acute cholecystitis It is a sudden inflammation of the gallbladder that causes severe abdominal pain. This disease occurs when bile becomes trapped in the gallbladder. The buildup of bile causes irritation and pressure in the gallbladder. This can lead to infection and a hole (perforation) in the organ.
Your doctor will do physical exams. Also blood tests may reveal higher levels of white blood cells, which suggest an infection, and elevated liver enzymes, which suggest a blockage or irritation of the gallbladder and bile ducts. Your doctor may order a radiology test to look for gallstones. Because the chemical composition of most gallstones makes them invisible on X-rays, other tests are used such as ultrasound and cholescintigraphy.
Ultrasound : This painless procedure uses sound waves to create images of the gallbladder and bile ducts. An ultrasound is usually the first (and often only) test needed to confirm that you have gallstones and cholecystitis. A gallbladder wall with a thickened appearance means you may have acute or chronic cholecystitis. Enlarged bile ducts suggest that a stone may have passed out of the gallbladder and into the common bile duct, causing a blockage.
Cholescintigraphy : This test looks for a blocked gallbladder or bile ducts. You are given an injection of a radioactive chemical that passes out of the blood into the bile ducts. A special camera takes pictures of the chemical’s path and can detect blockages in the flow of the chemical.
Cholecystectomy is the removal of the gallbladder due to stones which is one of the first laparoscopic surgeries performed on human. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy removes the gallbladder and gallstones through several small incisions in the abdomen. In emergency situations when the infection is severe, surgery may be more complicated and hospitalization period will be longer. Diabetic patients with gallbladder diseases should be operated immediately.
